Table of Contents
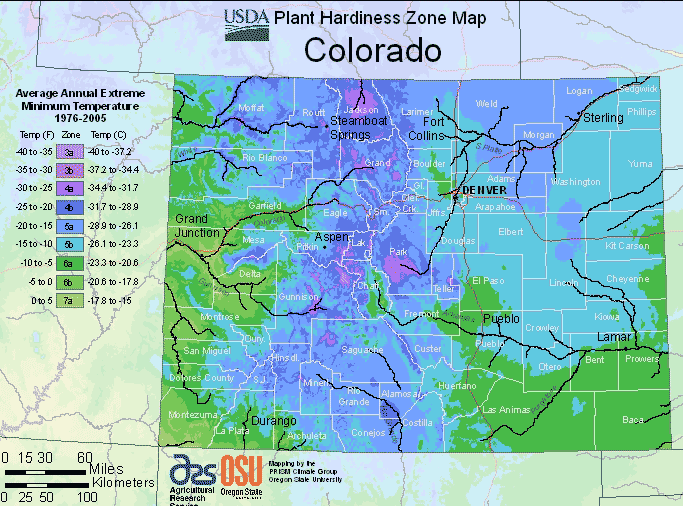
Characteristics of Colorado Planting Region
- cold winters,
- hot summers,
- low humidity
- wide diurnal temperature range.
Going up in elevation brings extra difficulties, such as unpredictable cold spells and unpredictable temperature swings.
Most of the state will have a high point of growth from June to August, characterized by long, hot, and sunny days.
Challenges of growing in Colorado
1. Shorter Growing Season
In Colorado, the best time for planting is June-August, though some regions may have a shorter window.
2. High Altitude
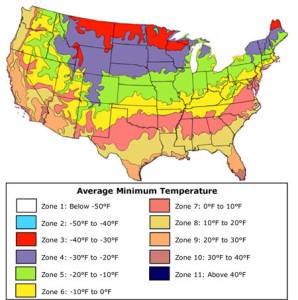
3. Temperamental Weather
The climate in Colorado is unpredictable. Dryness and wildfires could be prevalent in some years, while colder temperatures and extended frost seasons might appear in others. Keeping track of the weather is essential for a successful garden.
4. High Winds
The Rocky Mountains and cold pressure systems generate powerful winds that can reach 100mph. Without proper shielding, these winds can cause destruction to your projects.
5. Wildlife
Colorado is home to a plethora of gorgeous animals. Unfortunately, birds, deer, and more may become attracted to your garden and devour your hard-earned harvest. To ensure the safety of your plants, consider designing an enclosed garden.
Flourishing in the Rockies: Best Plants for Colorado’s Planting Zone
Here are some of the best plants to grow in the Colorado planting zone:
- Rocky Mountain Penstemon (Penstemon strictus): This native perennial is well-suited to Colorado’s climate and provides a burst of color in late spring. The Rocky Mountain Penstemon boasts striking blue-purple flowers that attract pollinators, making it an excellent addition to any garden.
- Colorado Blue Spruce (Picea pungens): This iconic evergreen tree is a staple of Colorado’s landscape. With its distinctive silvery-blue needles, the Colorado Blue Spruce adds a touch of elegance to any garden or yard and is highly resistant to cold temperatures.
- Gambel Oak (Quercus gambelii): As a native deciduous tree, Gambel Oak adapts well to Colorado’s climate and provides excellent shade during the hot summer months. Its autumn colors are particularly stunning, ranging from golden yellows to deep reds.
- Apache Plume (Fallugia paradoxa): A hardy shrub native to the Southwest, Apache Plume thrives in Colorado’s arid conditions. This low-maintenance plant features delicate white flowers that turn into feathery pink seed heads, adding visual interest to the landscape.
- Russian Sage (Perovskia atriplicifolia): Russian Sage is a favorite among Colorado gardeners due to its drought tolerance and striking silvery-gray foliage. This perennial produces tall spikes of lavender-blue flowers, attracting bees and butterflies throughout the summer.
- Firewitch Dianthus (Dianthus gratianopolitanus ‘Firewitch’): This tough, low-growing perennial is perfect for the Colorado planting zone. Firewitch Dianthus offers vibrant pink blooms and a delightful clove-like fragrance that adds charm to any garden.
- Blue Avena Grass (Helictotrichon sempervirens): As an ornamental grass, Blue Avena is an excellent choice for adding texture and movement to your garden. Its steel-blue, arching leaves sway gracefully in the breeze and remain attractive throughout the year.
- Hens and Chicks (Sempervivum spp.): If you’re looking for resilient and drought-tolerant plants, Hens and Chicks fit the bill. These succulents form rosettes of fleshy leaves and come in various colors, creating a stunning display in rock gardens or containers.
- Autumn Blaze Maple (Acer x freemanii ‘Autumn Blaze’): This hybrid maple tree combines the best features of silver and red maples, producing brilliant red foliage in the fall. Its adaptability to Colorado’s climate makes it a popular choice for adding vibrant autumn colors to the landscape.
- Hardy Ice Plant (Delosperma cooperi): For a splash of vivid color and ground cover, the Hardy Ice Plant is an excellent choice. This succulent offers magenta blooms that open in the sun and create a stunning carpet effect when mass-planted.
To ensure successful gardening in Colorado, it’s essential to consider factors such as altitude, microclimates, and soil conditions. Additionally, it’s crucial to select plants that can withstand sudden temperature fluctuations and adapt to both arid and alpine environments.
Before planting, it’s beneficial to research each plant’s specific care requirements and water needs. Proper mulching and watering techniques will help retain moisture and protect plants during dry spells. Additionally, employing natural pest control methods and choosing native or adapted species can promote ecological balance and reduce the need for chemical treatments.
In conclusion, the Colorado planting zone (Zone 5) offers a unique set of challenges and rewards for gardeners. By selecting plants that are well-suited to the region’s climate and conditions, gardening enthusiasts can create beautiful, thriving landscapes that harmonize with the stunning Rocky Mountain backdrop. Whether it’s perennial flowers, native trees, or drought-resistant succulents, the best plants for Colorado will add beauty and vitality to any garden or landscape.
