Table of Contents
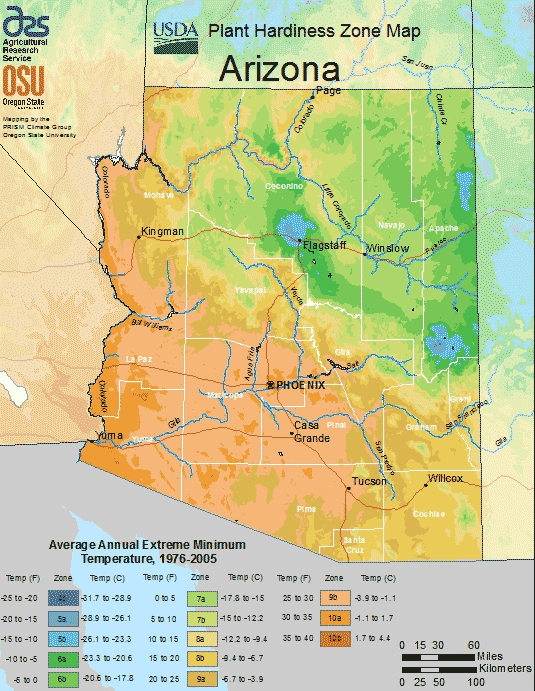
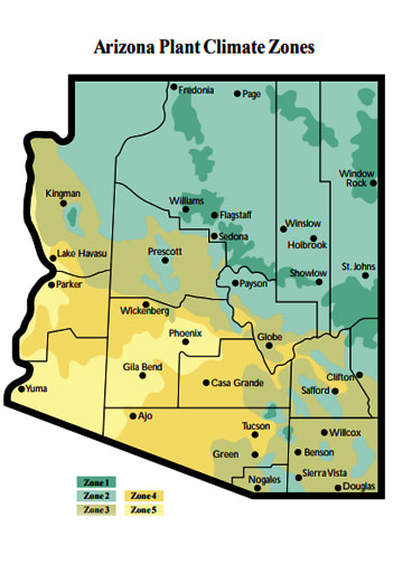
Characteristics of Arizona Planting Region
Natural disasters such as flash floods, dust storms, hail, and tornadoes can cause considerable harm and destruction.
Despite the difficult weather, the majority of the state will have a good period for growing from late January to early December, with an average of 316 days without frost
1. Extreme Heat
In Arizona, summer temperatures usually range between 90°F (32.2°C) and 120°F (48.9°C), which can be hard on gardens. A greenhouse is a great way to protect plants from the heat and help them grow.
2. Low Humidity
3. Intense Droughts
Year after year, Arizona is hit with intense, long droughts. To battle these difficult growing conditions, many gardeners use greenhouses to hold in moisture and make the most of the limited water for their gardens.
Flourishing in the Desert Sun: Best Plants for Arizona’s Planting Zone
Here are some of the best plants to grow in Arizona’s planting zone:
- Desert Marigold (Baileya multiradiata): As a native perennial, Desert Marigold is perfectly adapted to Arizona’s arid climate. This plant boasts bright yellow flowers that bloom throughout the year, adding a splash of color to desert landscapes.
- Palo Verde Trees (Parkinsonia spp.): These iconic desert trees are well-suited to Arizona’s planting zones. With their distinctive green trunks and delicate yellow flowers in the spring, Palo Verde trees bring a unique charm to the desert scenery.
- Agave (Agave spp.): Agave is a quintessential desert plant that thrives in Arizona’s hot and dry conditions. These succulents come in various shapes and sizes and make striking focal points in xeriscape gardens.
- Desert Willow (Chilopsis linearis): This drought-tolerant tree produces beautiful trumpet-shaped flowers that attract hummingbirds. The Desert Willow adds elegance and grace to any Arizona garden or landscape.
- Red Bird of Paradise (Caesalpinia pulcherrima): With its vibrant orange and red flowers, Red Bird of Paradise is a popular choice for adding a burst of color to the desert garden. This heat-tolerant shrub blooms throughout the summer, attracting butterflies and hummingbirds.
- Ocotillo (Fouquieria splendens): Ocotillo is an impressive desert plant known for its tall, spiny stems and bright red flowers. This unique plant adds a touch of drama to the landscape and thrives in Arizona’s dry conditions.
- Santa Rita Prickly Pear (Opuntia santa-rita): Prickly pears are well-adapted to the desert environment, and the Santa Rita variety stands out with its beautiful purple pads. This low-maintenance plant offers both aesthetic appeal and edible fruit.
- Yucca (Yucca spp.): Yucca plants are a staple of Arizona’s desert landscape. These striking succulents feature tall, spiky leaves and produce showy white flowers on towering stalks.
- Globe Mallow (Sphaeralcea ambigua): As a drought-tolerant perennial, Globe Mallow thrives in Arizona’s planting zone. Its bright orange flowers add a vibrant touch to xeriscape gardens and attract pollinators.
- Desert Sage (Salvia dorrii): This aromatic shrub is native to the Southwest and boasts silver-gray foliage and tall spikes of purple flowers. Desert Sage is well-suited to the dry conditions of Arizona and attracts bees and butterflies.
To ensure successful gardening in Arizona, it’s crucial to consider the region’s extreme heat and limited water availability. Xeriscaping, a landscaping technique that focuses on water conservation, is particularly popular in the state. Choosing drought-tolerant and native plants is essential for reducing water usage and promoting sustainable gardening practices.
Ample mulching and proper watering techniques, such as drip irrigation, help retain moisture in the soil and reduce water evaporation. Additionally, positioning plants strategically to provide shade for more delicate species can protect them from the intense sun.
It’s essential to understand the specific needs of each plant and provide suitable care throughout the year. Regular pruning, especially for desert shrubs and trees, helps maintain their shape and health while reducing the risk of pests and diseases.
Arizona’s planting zone offers a unique opportunity for gardeners to embrace the beauty and resilience of desert plants. By choosing native, drought-tolerant species and implementing water-saving practices, gardeners can create stunning landscapes that thrive in the desert sun. Whether it’s vibrant flowering shrubs, striking succulents, or majestic desert trees, the best plants for Arizona will add beauty and character to any garden or landscape, celebrating the natural wonders of the Grand Canyon State.
