
Roses are extraordinarily lovely flowers that have been linked to love for a very long time. They are one of nature’s most gorgeous creations, with over 150 different species (and thousands of hybrids), full flowers, alluring fragrances, and luxuriant foliage. You might be asking yourself right now, “What are the components of a rose plant?”
The stamen (male component) and pistil are the two primary (and most significant) components of a rose plant (female component). The petals, sepals, leaves, and stems are additional components. Each of them additionally has smaller components that work together to support the growth and development of the plant.
We go into greater detail about what each of these components contributes to the rose’s life cycle below.
Table of Contents
What are the Parts of Flowers?
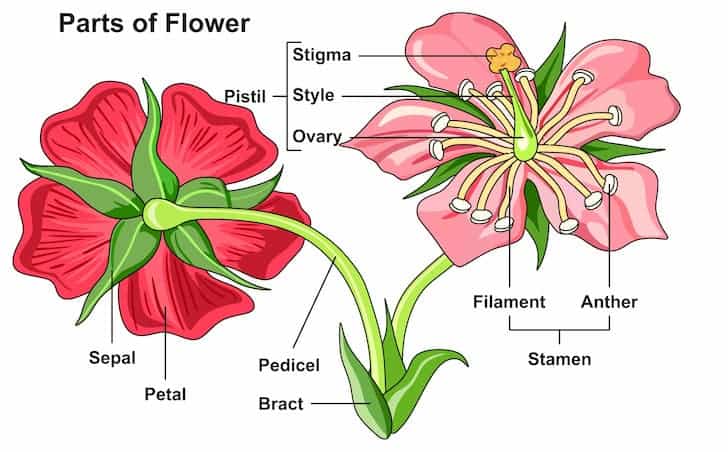
The Stamen
A flower’s male reproductive system includes the stamen. Both the filament and the anther are part of it.
The Filament
The stalk-like portion of the plant that connects to the flower’s base is called the filament. Additionally, it sustains the anther, which contains the pollen.
The Anther
The sticky portion of the stigma’s top is the anther. It is typically oval in shape, orange or yellow in color, and produces pollen that is vital to the plant’s survival.
The Pistil
A flower’s female reproductive system includes the pistil. The ovary, style (or stalk), and stigma are all parts of the carpel, which is normally located in the middle. A single carpel or a group of connected carpels are frequently referred to as a pistil.
The Ovary
The female egg cells, known as ovules, are found in the ovary, which is a component of the flower’s female reproductive system. The ovary may be found above, below, or at the point where the petals and sepals converge. Each ovary of the rose produces a ‘achene,’ which is a dry seed.
The Style
The flower’s long, slender, tube-like structure is known as the style. It ties the stigma and ovary together. For two reasons, the style is essential to the fertilization process. In addition to being the location of pollen tube formation, it also prevents incompatible pollen from entering the ovary.
The Stigma
The stalk at the top of the pistil is known as the stigma. It is a component of the flower’s female reproductive system and the site of pollen germination, which is crucial for reproduction and growth.
The Petals
The blooms of a flower are referred to as the petals. Cellulose and other organic materials make them up. In essence, they are modified leaves that encircle the flower’s reproductive organ. The corolla is the name for the petals taken as a whole.
The Sepals
The sepals are the flower’s surrounding greenery. Petals and buds, which are little knobs that eventually turn into blooms, are both protected by them. They also help the flower expand and provide support. Chloroplasts, the building blocks of sepals, are where photosynthesis occurs.
The Leaves
The above-ground vegetation’s leaves help in gas exchange and photosynthesis. They frequently are flat, green, and absorb the majority of the sunlight that the plant needs to grow. Stomata are pores-like openings found in many leaves that let in air and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
The compound leaves of roses are made up of several leaflets. Depending on the plant’s age, old garden roses may contain seven, nine, or even more leaflets. A short stem known as the “petiole” connects the top leaflet, also known as the “terminal,” to the other leaflets.
The Stipule
The stipule is the wing-like protrusion at the base of a flower leaf. It serves to feed the plant with energy and shield the developing leaves and buds. They also keep animals away from the flower.
The Auricle
The auricle is the term for the stipule’s very top or tip. It is the tiny, ear-like bump that can be found at the base of a flower’s petals or leaves.
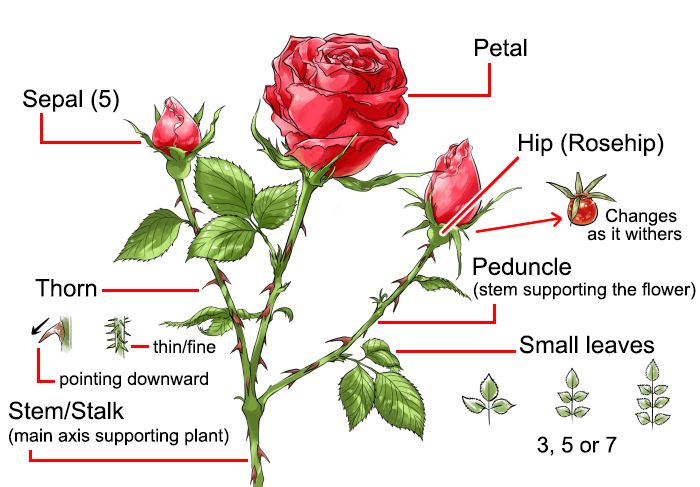
The Stems
Although some flower stems can grow underground, most are located above the soil’s surface. Depending on the class of the rose, different lengths of stems will be produced. They perform four primary tasks, which are as follows:
- raising the blossoms and sustaining the foliage
- moving water from the roots to the shoots, which are made up of the stems, leaves, and flower buds
- Keeping food sources’ nutrients in reserve
- creating and growing fresh living tissue
The junction of the leaf and stem is the source of new growth. The bud eye is what we call this. The peduncle is the portion of the stem that extends from the tallest point to the bloom itself.
The Peduncle
The thornless, soft-wooded portions of the stem known as peduncles vary in length and thickness depending on the species of rose. The bract is a little, almost leaf-like structure that is located halfway down the peduncle.
How Many Ovules Does a Rose Have?
An ovary can be found in each pistil of a rose. Numerous ovules can be seen inside each ovary. Some plants’ flowers can contain as many as 1600 ovules!
How Many Leaves Does a Rose Have?
In contrast to stem or “wild” roses, which often have seven leaves per stem, garden roses typically have five leaves. The flowers of cultivated roses contain multiple sets of petals and twice as many leaves.
How Many Petals Does a Rose Have?
The precise number of petals of a rose is unknown. Typically, a “wild” or “single” rose has one row of five petals, but they can have as many as twelve. The “rosa sericea,” which has only four petals, is the exception.
“Semi-double” roses are those that have thirteen to twenty-five petals arranged in two or three rows. Roses with more than 25 petals arranged in two or three rows are typically referred to as “double” roses. These include roses called “tea” or “china,” for instance.
“Double” roses are those that have more than 25 petals arranged in three or more rows. “Very double” roses are extremely large blossoms with 45 to 50 petals arranged in multiple rows. The number of petals in certain mutant species may be greater (or smaller), but they almost always occur in multiples of five.
How Many Pistils Does a Rose Have?
How Many Sepals Does a Rose Have?
Sepals on roses normally number five. The lone exception is the “rosa sericea,” which has only four sepals, identical to its petals.
How Many Stamens Does a Rose Have?
There are at least five stamens in every rose, but most have many more! Almost always, there are multiples of five stamens. The type of rose will determine how many stamens are present overall.
What Are the Characteristics of a Rose?
Regarding the rose, there are specific qualities. They consist of the following:
- has many stamens.
- has leaves that develop on the stem in an alternating manner.
- symmetrical in design
- consists of unconnected petals that are multiples of five or five
- features thrones or prickles on the stems that can be used to distinguish one species of rose from another. These thrones or prickles can vary in size, shape, and number.
- has sexual organs from both sexes
- has many hues, including red, pink, yellow, and white.
Summary
In conclusion, the size and color of the blooms on roses are frequently used to classify them. The stamen (male element) and pistil are the two major components of a flower (female element). The petals, sepals, leaves, and stems are additional components. Each of these features has smaller components that work together to help the plant grow and reproduce.
Understanding and appreciating the numerous components of this lovely flower can only heighten your admiration and enjoyment of it. So accept the proverbial advice to “take time to stop and smell the roses” and do so now.
FAQ
What is the filament of a rose?
The stalk-like portion of the plant that connects to the flower’s base is called the filament. Additionally, it sustains the anther, which contains the pollen.
What are the five external structures of a rose plant?
The components of the plant that are visible from the outside are its exterior structures. They contain leaves, stems, roots, and flowers. The growth and survival of the plant depend on the leaves, stems, and roots. The wild rose plant also possesses floral structures that enable reproduction.
What are the structures of a rose?
The stamen and pistil, which are the male and female components, respectively, are the two main components of the rose plant. Petals, leaves, and sepals are additional components.
What is the structure of filament in a rose?
A thin stalk called the filament protrudes from the flower’s base. The sticky, bulbous portion of the filament at the top known as the anther is what produces pollen. The pistil, which also includes the style, stigma, and ovary, is the name for the female reproductive organ.
